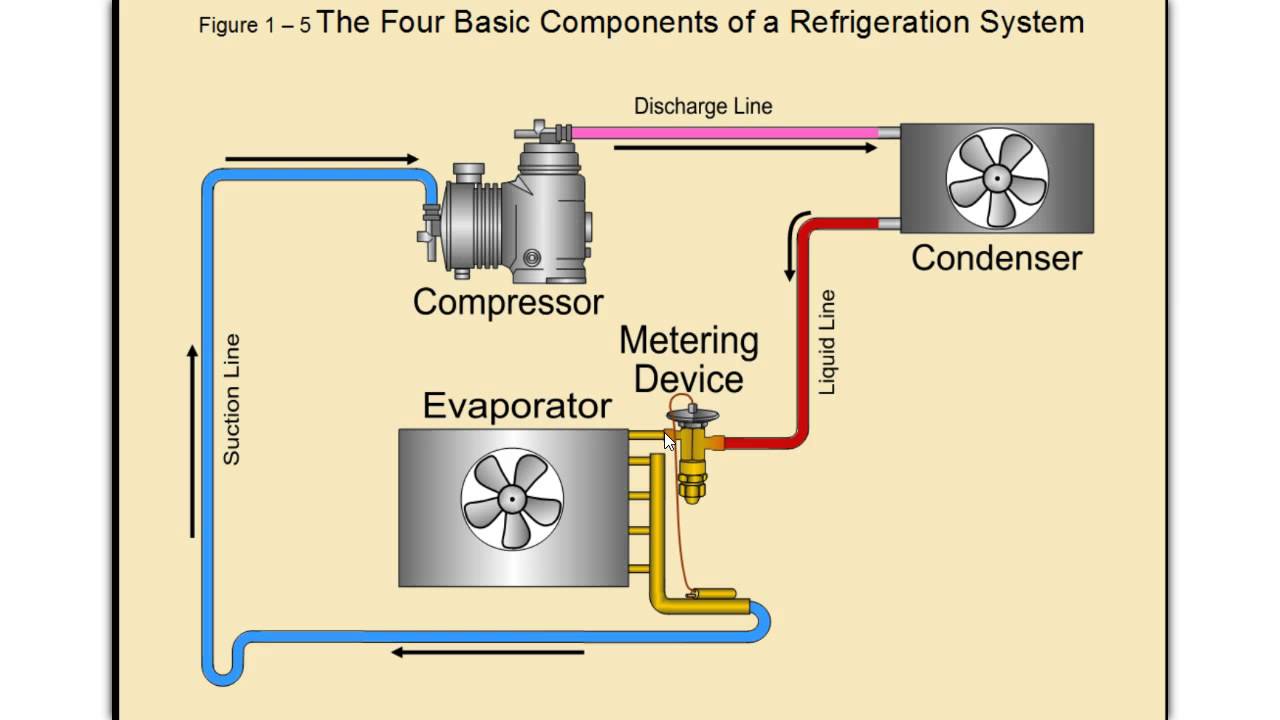
Refrigeration fundamentals:
- Refrigeration:
It is a science of providing and maintaining temperatures below that of surrounding atmosphere.
- Ton of Refrigeration (TR):
It is the quantity of heat required to be removed from one US
One US
Latent heat of fusion of ice = 144 Btu / lb
Therefore,
1 TR = (1x2000x144) / 24
= 12000 Btu / hr
1 Btu = 1.055 kJ
Therefore, 1 TR = 12000 x 1.055 / 3600 = 3.517 kW
1 kcal = 3.968 Btu
Therefore, 1 TR = 12000 / 3.968 = 3024.2 kcal / hr
Note:
i. “ton” is unit of heat whereas “tonne” is a unit of weight.
ii. “TR” unit is used in US, UK and India
iii. Due to fact that refrigeration was first produced by ice, the refrigeration effect of refrigerating machines is compared with refrigeration produced by ice.
- Coefficient of Performance (COP):
COP = Refrigerating effect / Work input
Relative COP = Actual COP / Theoretical COP
- EER (Energy Efficiency Ratio):
EER = (Cooling capacity in Btu / hr) / (Power input in watts)
- SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio):
The anticipated performance of a refrigerating device, over an average season is called as SEER and is expressed in same way as EER.
Note:
a. COP is dimensionless whereas EER & SEER are not dimensionless.
b. COP is important from designer point of view.
c. EER is important from manufacturer point of view.
d. SEER is important from customer point of view.
e. EER = 3.412 x COP (In Btu system)
f. EER = 3.6 x COP (in SI system)
Air conditioners have EERs ranging from 8.2 to 10.5. On the other hand, water cooled system has EER = 12 or even higher than this.
- IPLV (Integrated Part load value)
In central air conditioning plants, water chiller is one of the main components.
IPLV measures the efficiency of water chiller under variety of conditions i.e. when the system is operating at various capacities such as 25 %, 50 %, 75 % and 100 % and at different temperatures. IPLV rating is given in kW / TR.